Assistive Technology A Toolbox for Student Success- Tammy Dupre- LA Accessible Educational Materials
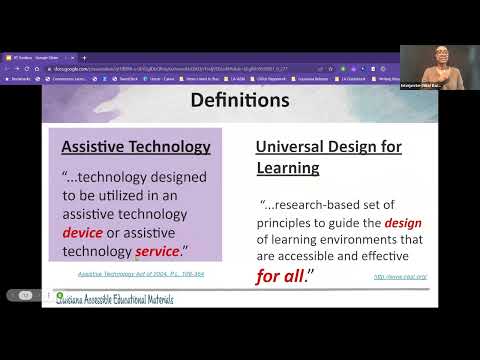
my hair I have a dark short hair uh and a gray sweater and a black dress oh okay so I was gonna wait for the I don't see that okay yeah see The Interpreter I was looking for The Interpreter okay um so hi like Bambi said I've been friends with her for a very long time um I've been working in the field of assistive technology for many years and uh I am a special education teacher and I'm here to talk to you today about assistive technology and how it can remove barriers for student achievement um and it also can increase Independence and improve their academic performance so I have right here a QR code on my screen if you would like to join our mailing list you can scan that and sign in and we'll put you on our mailing list our services are free to everyone we do professional developments we have a lending library I'm going to just go on to the next slide um this is a link to the presentation uh Bambi has another place to get the presentation but if you wanted to scan this link you could also get the presentation and all the information that I'm going to be sharing with you from this presentation link and you can follow along if you have a device or whatever you could just follow along with me okay so like I said I work with the Louisiana accessible educational materials program and um we are again a free resource to parents families Professionals in the kindergarten K through Early Childhood K through 12th grade sector so um anything that pertains to education and school we can definitely address any kind of needs that you might have if you are you know if you're a parent or if you're a professional we help both sides of that continuum so our website is on the screen it's ssdla-aem.org and you can see all of our ongoings and all of our information from our website so we have service centers around the state of Louisiana um we are right now existing with one two three four five of them and our main office is in Baton Rouge at the school for the blind and deaf so if you wanted to get in touch with us there you could also in all of our contact information on our website so what I wanted to do with the crowd first was to maybe get a little poll to see who I'm talking to and so if you wanted to you could use your cell phone or you could go to a a new tab on your browser and go to slidio slido.com and type in 247396 and I'm gonna just post a few questions and then you could answer through that uh portal okay so I'm going to give some time for people to just kind of go out to that site or scan the QR code and then I'm just gonna say three questions just to kind of get a feel of who I am speaking to a few more minutes before I started okay so my first little question is where do you work in whenever I say where I just mean like what part of the state or you can put like the place that you work for too that's fine okay cool some early steps people well okay got some people here from Mississippi wow okay so next question is what is your title like what do you do within your your job that you're currently in like what is your so it's cool that I'm talking seeing a lot of program managers and coordinators they'll better share the information that I'm sharing with you guys to different schools or people that you might uh be networking with just to know about the information awesome a lot of coordinators okay and last question how would you rate your knowledge on assistive technology awesome very experienced people maybe some a few newbies too hear me I pressed five without that but the question was I thought I was rating you oh no imagine the crowds uh participation I mean uh a knowledge about assistive technology and you probably know more than you think you know about it um a lot of times we find that out that a lot of people know more about it than they think they know because they never really called it dots you know so I'm gonna talk about some examples of what it could be and then you'll be like oh yeah I know about that so kind of Midway all right so let's get into objectives so what I want to try to do here today is to increase everyone's knowledge about assistive technology and uh and how it creates the least restrictive environment for the student with special needs we're going to look at a framework to guide decision making for assistive technology and we're going to look first a look at some available support for our general education curriculum and access and participation um for students who are um have an IEP or just might be needing to be included in gen Ed environments okay okay so these are the laws that mandate assistive technology to be considered and it's been around for a few years now this is not a new thing it's always been a part of our consideration process within the IEP process and so we have to just remember that it is the law and we do need to talk about this and there's a there is a need so what is assistive technology so I let me make sure that when I shared my screen share the sound so that you can hear um and I'll put everybody can turn on their own captions correct I'll put the captions in the video on too we all like to do things like color and read and use a computer it's how we play learn work and get things done but when a disability makes it hard to do something we'd like to do we need a little help luckily there's a solution welcome to simply said understanding assistive technology assistive technology or at is anything that helps you do something you couldn't do otherwise like walk run communicate and more these helpful tools can be as simple as a foam grip that makes it possible for a child to grasp a crayon and create art as common as glasses that make it possible for a student to read and learn or as sophisticated as software that makes it possible for an employee to convert their spoken word to text on a computer screen and succeed whether you're young or old male or female whether you've had a disability from birth or developed one over the years at can help okay so just a little a little quick video about what assistive technology is so like I said you probably know more about this than you think you did we all like to do sorry about that my color all right so here are the technical definitions of assistive technology I'm not going to read them all to you but basically assistive technology is a device uh and a service or it could be either R it could be a device or a service um so it's it's more than one thing uh Universal Design for Learning I'm going to kind of go into that definition a little bit and show some examples of that so Universal Design for Learning is a framework to improve teaching and learning for all students and it's based on how everybody learns how they take in information how they express information and um I'm going to show you a little cartoon picture here and the picture is a picture of a guy shoveling off sand off of a stairwell and then there's a ramp on the right hand side of the stairwell that also has snow on it and there are children at the base of the stairs and the ramp waiting to enter into the building and one student is in a wheelchair the rest of the students are standing and walking and the captioner reads could you please shovel off the ramp the student in the wheelchair says and the CH the person shoveling the snow says all these kids are waiting to use the stairs when I get through shoveling them off I will clear the ramp for you and the students in the wheelchair says but if you shovel the ramp we could all get in and so basically this is a great and a great representation of what Universal Design for Learning could do is that if you design the instruction from the beginning accessible to all then everybody gets something from it as opposed to it being only accessible to students who take that information in in a certain way okay so just looking at Universal Design for Learning and so every student succeeds succeeds Act is um an act that was passed that and it basically what it states is that all assessments must be developed to the extent practical practical practice sorry the word is like getting off my tongue using the principles of assist of a Universal Design for Learning so we want all assessments to be accessible to all students and um there there is a law that protects all students from not having uh to take tests that are not accessible all right so this is one of our favorites at people out there his name is Christopher bougay he has written a book called the new assistive Tech assistive technology has changed over the past years um it's it's gone from being this thing that's only special for certain kids to being universally designed for any kid to use and so um the reason that this has changed is because of the advances in technology and so what I want to do is I want to show this really great little video about um what what teachers need to do they need to become educational um experienced designers so it's teachers that have to change their instruction so that they can reach all students so this student uh right here I'm just gonna go ahead and play this video and maximize this time I'm Tucker and I'm a student like many kids my age I enjoy many different things like playing soccer dog and like playing video games but what I like to do most is learn new things school is a place where I can do just that teachers I thought I'd make this video to help you know what I'd like this way you can help me learn how to learn I made it into a four-step process step one I love to solve problems not just memorize facts I have all my facts right here what I really need to know is how to find the facts prove they really are facts and find out what to do with them also the more real the problem the more interested I am helping others feels great step two you always tell me what to do how will I ever learn from myself I learned to make good decisions by making decisions I'd love to make my own choices one of these decisions includes the technology I use please design lessons with some flexibility everyone learns exactly like I do technology allows you to provide options for everyone step three I love to make things sometimes this is with my hands and sometimes this is with technology I'm feeling out where she's really isn't that interesting creating things whether that be a video podcast story cartoon or anything else that will be seen and used by others is super fun what are we gonna make together step four finally and most importantly I wanna have fun I don't want school to feel like a chore I have enough of those at home I want learning to be fun if he follows steps one through three then you can't go wrong and if I'm having fun then chances are you're gonna have fun too now for a quick review one introduce me to real problems to solve two guide me to help me make my own choices by providing options for everyone three give me an opportunity to make stuff four let's all have fun instead of thinking of yourself as a teacher they can be yourself as an educational experienced designer what kind of awesome educational experiences can you design I along with my entire generation can't wait to find out okay so I just wanted to show that because I feel like we need to kind of shift our thought process as Educators to designing more interesting things for kids to be engaged into as opposed to worksheets so I also want to show um this next slide and uh play this game called name this disability on this slide there is a picture of a worksheet with five questions and um the student has filled out the answers and they have written to the best of their ability so uh in the chat box can they chat can they can they type in the chat box go ahead and put in the chat if you can um what disability you think this child has by looking at this worksheet I think you can type I'm not seeing people type so I'm not sure if you can type oh it's in the Q a okay sorry okay I see some people say in dyslexia some people said autism um some people one person said cerebral palsy okay let me uh how would you even know someone said I cannot tell those are all great answers okay let me move this out the way so so the answer is the child doesn't have a disability um that this this work this work right here is produced by a typically neurotypical child in sixth grade with no known disability and the main concern with this example is that the students uh is now that the students abilities are learning but it's the design of the lesson did the students uh did that this activity really um was it really something the child was able to show would they know when when when it's really hard to read what they said um this should not be the only way students are showing what they know by answering questions on a written test they should be able to show things that they know in other ways besides just answering questions on a test so um um so I just wanted to kind of show you that lots of kids out there are performing like this on written tests but they they probably could do a much better job if they were given alternate ways to show that they know like maybe creating a video or maybe doing a PowerPoint presentation or maybe creating something with their hands you know so just showing that example just to kind of give you an idea so this is the international Society for technology using Educators standards for education and so we want to be able to shape and Empower learning through technology we want to be able to um advocate for Equitable access to technology and digital content and learning opportunities to meet the needs of all students and could do that actually a little bit better when you have technology in place because you can really customize each individual's experience using technology um you can collaborate and you can create authentic learning experiences and by leveraging the technology and so these are the standards for education and Educators using technology I also wanted to kind of just let people fill out a survey to show me what their with their children if you have children in school or if you have uh if you work with the district what technology do they use you know now ever since covid happened a lot of districts had a lot of funding to some districts went one to one one computer one child um so I wanted to kind of like do a little survey or let you do this survey just to kind of um let you comment about what what is the the technology usage in your District because we have noticed over the past couple years after covid that there was a big uh push to use technology with students and then once we came back face to face everybody went back to paper pencil not everybody that's an exaggeration but um a lot of people went back to paper pencil because that's what they're comfortable with but if you notice on this slide right here the Department of Education has document called building digital literacy it's very interesting to see what is expected what digital skill is expected at what level the child is in from kindergarten through 12th grade if you take a look at some of these um and some of these uh skills you'll see that keyboarding and the proper use of posture and how to locate letters and numbers on the keyboard is introduced in kindergarten and it's mastered in fifth grade so the expectation for kids learning to type with a computer at the at the Department's level is that they get keyboarding from from uh they learn how to do that in second third fourth and they Master it by fifth grade how many kids do you know uh are are have mastered typing in the fifth grade the reason that they are not able to do that is because they're not begin being offered the opportunity to do that through second third fourth and fifth grade so this this um technology Readiness diagram is very eye-opening it goes into word processing spreadsheets and tables and charts and graphs to access numbers and and to uh crunch numbers so um it's it's a really interesting document that the doe put out and I want to say it they put it out there's no date but it's actually been out for a few years now and so that's um it's called building digital literacy and it's like I said it's very eye-opening um example of what kids should be able to do at what age okay so um assistive technology consideration is part of the IEP process and it is the ongoing process that the IEP team considers for the student uh what kind of assistive technology they might require to achieve their goals and objectives and to and to be in the least restrictive environment um their uh everybody on the IEP team should be commenting and should be uh giving their opinions as to what technology or what tool the student could use to be more independent it uh it should happen with every IEP so every annual IEP you should consider the use of assistive technology and that sometimes will change sometimes it will grow sometimes you will reconsider what what they've used in the past if it's no longer working and um maybe something new came out that the the team wants to try with the student to um promote their independence in the classroom setting and it is legally required to do every IEP meeting a lot of times what we find is that the IEP team says oh they don't need that and um that's not how you consider you don't consider it by just saying the child doesn't need anything um the child didn't need anything then I'm not sure why they have an IP so uh there is a framework for consideration called the set framework and I'm going to talk a little bit about that of all students with disabilities should be considered for assistive technology the common area era in this is that only students with the severest disability get considered but all kids that have an IEP there should be a conversation about assistive technology and how it can help that child there is a range of assistive technology um it starts from low Tech to Mid Tech to high tech and low-tech is basically paper products paper things that could help children like um anything from a paper-based communication board to a Venn diagram um and then mid Tech is battery operating devices that might want to help students um with spelling maybe high tech would be a computer or maybe even a high-tech communication device um so the set framework like I was saying the set framework stands for student environment task then tool and it was developed by Joy Isabella and I have a resource here I also have a link to the IEP forum in sir and um so whenever you consider the assistive technology first you look at the students and their functional area or concern of need and it could be from academic to cognitive communication motor self-help social um you want to also consider their current strengths and weaknesses and then when you figure out where they are needing assistance you would look at where is the environment that they're going to be in like how can you rearrange things how can you rearrange a desk what kind of support can you give them in certain environments and then what materials and Equipment are available for all students because you might not need to make that many accommodations if the students already have materials and equipment that everyone is using um attitudes expectations and those environments um and then what is the task the student is trying to complete that they're having difficulty with what are all the other students in the classroom doing um and then you want to make sure that within that task the student is able to um participate and do something within that task to their ability and then what tool could they use to help them be successful with the task so there's lots of different tools out there okay here's just some different ways to be able to frame the question as to say what assistive technology device or service would help that child reach the goal um so again thinking about what is their present level of performance um how is their disability affecting their performance um where does the task need to be done what are the strategies that are you being used currently and then are there any specific tools or strategies we can use okay so here is the big question on the IEP um that's very very very important and it is if a child has limited or no verbal skills how will they communicate in the classroom with the peers and the teachers um every student should have some type of communication system they are learning if they are non-verbal whether it's just a simple uh array of core words that they are trying to communicate the teacher should be modeling that type of communication in the classroom that they are expecting the students to become fluent with so uh what we see a lot is that the child that is non-verbal doesn't have any communication system that they are learning and uh what ends up happening is that child ends up having behaviors that arise and then everybody wants to have a behavior plan when they should have had a communication plan filled out and so right here on my slide I have the tools for developing communication plans from the Department every school district has their own way of addressing the unique needs of nonverbal students and so this is a suggested way to consider communication for a child who has having communication issues and so it's a it's about a 15-page document but the actual communication plan starts on page nine and it's only three pages so the first eight pages are all about that conversation that the IEP team would have to talk about the unique needs of the child as it pertains to communication like for instance what language is spoken what language is spoken in the home so if the child is coming from a different a home with a different language other than English then the IEP team and everybody working with the child needs to know that the child is first language is Spanish or Laotian or whatever so that you can understand that the child might understand what you're saying if you speak it to them in their native language so all of this all these questions in this document are really critical to considering the unique needs of that student and and how um how you can approach teaching communication uh method to that child in the classroom so that's there for your information all right so the next thing is uh Student Response mode so when students are being uh Statewide tested the teachers have to designate what will be their response mode if they are non-verbal how would they say that's the one that's the choice I want that's the answer I want to choose so these are just some examples of how the child could say that in the class while they be in questioned or even on standardized tests so I just wanted to share that with everybody all right so some more examples of assistive technology we in our program have an assistive technology loan Library um if you click on this picture in our presentation it'll take you out to our inventory on our website and it'll show you by location all over Louisiana we have five different centers and I'm sorry one two three four five yeah five and you can depending on where you're at in the state you can choose by location to see what kind of inventory assisted technology inventory we might have that the school district could check out we typically check out two school districts for the for the purpose of them trying before they buy for that student um some of these devices are a little expensive and if if uh IEP teams are unsure of what is going to be the solution for that task for that student um they can definitely try some of these devices out before they actually go and um purchase that for their Library um so this again is on our website and anybody could anybody could peruse this library but typically we check out to school districts so that they could try before we bought but they could try before they buy okay so what I wanted to do today um as I have enough if I have enough time is show some examples of accommodations and modifications within a curriculum um so you can kind of see what teachers could do to modify and accommodate for students specific needs and so what I'm looking at here is the ldoes ELA guidebooks English language arts curriculum and the particular unit is uh the line which in the wardrobe and I think it's a sixth grade unit if I'm not mistaken and so I'm just going to take some lessons and an activity from this um from this example and show you how you would apply assistive technology for student outcomes okay so for the purposes of my examples I want to explain when I say high incidence disability what I mean and when I say low incidence disability what I mean and so I just want to be clear when I say high incidence disability um I'm talking about students maybe with dyslexia um these are students that have a disability that's a larger part of the population than low incidence disability when I say low incidence disability I don't mean low cognitive necessarily because that child could be either hearing uh deaf or they could be visually impaired and if they are then they are academically typically those students are academically on level um and it just means that they it's a low incidence disability that means that it's not a large population of students um and their disability doesn't um it's it's it's more common with like uh hearing impaired deaf or a significant cognitive or physical disability and it's just a lower incident of the population of students is basically what we're talking about okay so looking at reading difficulties typically students in classrooms have issues with these areas when it comes to reading so phonemic awareness which is the ability to focus and manipulate on the phonemes of the spoken word phonics is the ability to associate the sounds with the letters and use these sounds to form the words and then vocabulary is identifying the meaning of the words and using these words appropriately within the text and then comprehension is understanding um the intentional interaction between the reader and the text that conveys meaning so these and then fluency is just being able to read fluently and understand um what it is that you're reading as you're saying the words so these are some of the areas that usually typical typical students are actually students who struggle have trouble with all right so I have a little handout so as I show these different assistive technology strategies and tools if you click on this handout you will see that the accommodations are listed in the First Column the tools and strategies are listed in the second column and then there's a notes column in the last column and I've put in here uh if it's a response accommodation or a presentation accommodation um and this is actually taken from the IEP this third column so um that's just a resource that you can share with anybody who is kind of wanting an example of these kind of accommodations all right so this slide is a slide that just shows hold on one second it shows what uh the teacher would be doing with the students in this lesson they're going to be reading the chapter from chapter one from The Lion the Witch and the Wardrobe and the clock the class is going to read and work with words discuss and express understanding and the summarizing activities the second card shows what the students need for the lesson so they're going to need a copy of the book they're good in in the in the in the way that they can read it so like if they're um if they're visually impaired they might need a braille copy um some of the students if they're not reading on level they might need a digital copy so that they can listen to it being read to them uh they also need a reading log where they're going to be taking notes and they're going to need their uh semantic map their handout that they're going to be doing okay so this is what a gen Ed lesson uh would look like now so here's what maybe the resource teacher might do to prepare for that student to be included in that lesson and I'm talking about high incident supports for students who are maybe dyslexic or they may just be um reading below level so a digital digital formats of the text are available sometimes you can just Google that title of that book and sometimes you'll find the digital text just out there for you to grab this example that I put in my presentation is actually from Canada and uh it goes out to this Canadian website and it's the entire text for the line the Witch and the Wardrobe so um basically some different things that teachers can do to make this um accommodating for the student without changing what it is that they are doing uh Project Gutenberg and Bookshare are two resources that you can uh get digital materials from and students that have print disabilities meaning they cannot derive meaning from just looking at print on paper uh will qualify for uh Bookshare and school districts do not have to pay for this resource it is a free to any child with an IEP with a print disability so um school districts typically have a Bookshare policy and they have students that they have a a policy where they certify students for Bookshare and they're able to get all their books in digital format for free to the schools okay so what I would like to show is uh different ways to simplify text if you have students that are um if they visually look at text that's too close together they kind of shy away from that they don't want to look at it because maybe the font is too small or the words are too close together so uh there is a Google Chrome add-in called Mercury reader and uh this is oops sorry about that whenever you have that loaded on your computer it looks like a little spaceship and I think it's right here it's kind of grayed out online so let me click off of it okay sorry that shouldn't have happened let me just go through my presentation back to the slide I was on sorry kind of reset my uh slide back sorry about that guys okay so what I'm going to show here is I have the digital text up and if you could see the digital text it's like small and all the words kind of jumbled together with this Google Chrome add-in when I click on it uh it gives me some features that I can make the text with a different background um if I go into this right here I could say I want it large medium or small text size I could change the the text fonts really quickly and see how I could change the color so this is just a Google Chrome add-in that allows me to change the way text looks immediately without having to copy it into a different framework and it's called um it's called a Mercury reader and it's one of many Google Chrome add-ins that you could put into this student's Chromebook that allows them just to see the text in a different way and a lot of times students say oh I like the way that looks better and they're not um they don't shy away from looking at that text another thing you can do to simplify um text is use the free tool rewordify and so this tool will change um what the student would be reading by simplifying some of the vocabulary on that on that uh on that document so what I could do is I could come in here and I could grab the first paragraph of what they're reading copy it and then come back into this tool called rewordify paste it in there and then I could sell it at what level I want to rewordify it okay and then when I hit rewordify it it rewordifies it down maybe a reading level but I can look at the stats here so that gives you the stats of the reading level and it's all free you can teach to the students how to rewordify paragraphs if they're too difficult or they don't understand the words and what happens is they'll take the word and this was air raid and sometimes they'll rewordify the word inside and when you click on it it'll tell you the original word so it's exposing that child to the vocabulary and the words within the Gen Ed text but then it's giving that definition within that same view so uh you're still exposing that student to that content you're just giving them a little extra something by giving them that definition built into the paragraph and again it's rewordify.com and it's
free for students and teachers to use whenever they're getting exposed to new uh texts that they might not know all the vocabulary words um and it and it would be hard for them to follow because they don't have that prior knowledge okay color coding materials is another way to create a combination for a student um just by using color coding and so I have an example here of color coding and using color coding to help students uh inter you know just see see materials in a different way okay so this is the a reading combination log with color coding and so notice how in the chapter the table of contents is color coded and as you go through the document your con you're using color coding just to kind of help the student out okay so looking at let's prepare for the same activity for low incident students what would accommodations and modifications look like for a student maybe with a little bit uh more needs and so this example is being able to create a picture a picture dictionary with the vocabulary from the reading really quickly using a tool called read write for Google and so what you're seeing on the screen right now is you're seeing a gif or a video I think we may have lost Tammy I think we may have lost Tammy but we'll we'll work on getting her back on Brenda I see you have your hand raised um if you have something you could type it in the Q a okay [Music] we're just waiting for Tammy to to get back ah there's Tammy sorry guys my computer just went black you got back to us quick yes it just totally went black and I was like oh God here we go we didn't say the technology prayer okay here we go so I think we're back you see my screen now yes everything looks fine okay all right um okay so what I was talking about was uh read write for Google has a tool where teachers can go in and automate a picture dictionary so what you're seeing on the screen is just the steps to go do that so that teachers can create these accommodations and modifications really quickly because it does take a lot of time and preparation for uh for teachers to give students the materials that they need in the way they can take them in so another uh idea is I want to just show you this adapted book and so what we did was we took the same reading that the Gen ed students were reading and we input it we put in pictures and every time the character was mentioned we put the characters on that same page so we didn't change what the students were being exposed to we just added pictures that supported what text was saying for those students that understand better through pictures and so every time the character talks in the paragraph We would put the picture of that character before what they were saying so this is just an example of that first chapter's reading and what uh material could look like for a student that's maybe included in this gen Ed setting for this lesson so just that little example and then kind of summarizing with pictures this whole paragraph what what you really want the student to understand from that paragraph sorry okay so showing the next uh part with reading so high incident supports for reading and highlighting using Google read write for Chrome just showing how to use a masking tool so that student could be looking at that section of the text and being able to just highlight different parts of the text because all the students have to highlight words in the text as they read it words that they may not know words that they might need to look up as they read through the text and use their Reading Guide or their reading tool they have to like find vocabulary words so just teaching them how to use highlighting tools to be able to pull out words that they have to Define so this again is a read write for Google Chrome tool that we're looking at and it's using screen masking and highlighting these are all different tools that teachers can you let students utilize while they're learning new materials and these are accommodations because we're not modifying what the child is being expected to do we're just giving them tools to better do it a little easier oh magnification keyboard shortcuts is also a modification an accommodation using a reading filters and color overlays and then a highlighter tape is a low-tech tool if the student had materials that were paper-based they could use highlighter tape and then again adapted pencils so this is a you know just a way to have them write with pencils that are more easily to grip if they're using paper okay so for low incidents let's read section you can put in um something like the pin friend in place the pin friend is an audio pin where you can record um a word or a sentence and when the pin when you show the pin the yellow yellow highlights it reads back that audio message so you can program the text if the child doesn't have a computer you could program some little uh places in the text where the child reads it out loud or that it will read out loud to the student um looking at defining words a student that might be a lower cognitive might just be looking and defining one word out of the text and so for this example we chose inquisitive which means curious and uh we just let them pull that picture off of the text and put it in their words to learn so this is how we adapted it for a student with maybe lower uh incident supports and their reading log would have velcro as opposed to pencil because they're not really working on that type of thing um here's an example from uh misunderstood the website misunderstood and it's hyperlinked here so when I click it it goes out to understood.org and this is a great website that has a lot of resources for children that struggle in school settings with various exceptionalities and this is just an example on how you would use assistive technology for the writing process what do kids struggle with um who do they who struggles you know what kind of tools so when you scroll down it'll tell you it has this really cool little generator right here too where you can say what role you're in what do you need help with is it Reading Writing so like when you select the role it says parent caregiver educator I'm here for me so students can use this too and then what do I need help with uh and these are all the behaviors I might have I might struggle with distraction following instructions stress anxiety managing my emotions and so you can save that and then here's the learning like is it reading is it uh math is it school struggles and then and then you would say what are you trying to do say organized taking talking and understanding and then you see when you click on see my resources what the website will do is it'll generate a list of all kind of resources that pertain to your needs so it's very cool on their website to be able to get information um around that certain disability and what is it uh with the characteristics are and stuff so for writing here are some handwriting tools like pencil grips and then keyboards touch screens dictation being able to talk into a computer and let it type what you want to say that is an accommodation for students who have trouble writing with their hands or they can't spell dictation can be an accommodation for that student uh word prediction so like when the student is typing we all use word prediction whenever we type on our cell phones so uh that's also an accommodation and then using spell check or grammar check using 10 text-to-speech to be able to hear back what you type that also could be an accommodation and then of course for those visual Learners using graphic organizers to organize your um thoughts and ideas so this this website is a really great website it's called um understood.org this is the home uh page of it and there's a lot of really cool examples of students on here that they'll uh they can show you like you know this is a student that has this exceptionality here are some things that they struggle with and here are some solutions that you could maybe try to help that student I see that I'm almost running out of time I'm almost finished okay so if students with significant disabilities like how do they write when they don't know what letters mean so here's some thoughts and ideas um a company has put out their action dictionary this is the ablenet company um and they have this action dictionary that shows what an act like what is the child trying to do and how can they do that action so for example they could tally to write they could have a list of things that they'd choose from and they could tally like which ones they want to choose they could Circle what it is they want the ending sentences that they want to write um they could record if they speak they can just record their answer or they can record what they want to speak they can choose from an array um or they can stamp if they have that ability so um I do I do have a link in that in that slide to get to this if you have an iPad you can um download this whole entire dictionary it is free and it's really great for those teachers teaching those kids that don't hold a pencil how are they going to do these school-based things a lot of kids have a lot of trouble with being able to do something that's School related because they just haven't developed that skill yet so this is a really great um resource okay so just as a summary uh using a comprehensive approach uh like for students if they can just listen to an audio book with social studies content they can answer related questions based on that and basically they're not they're not being assessed on their ability to read but they're being assessed on their ability to listen and and and come back and answer questions about what it is that they heard so um if you're not teaching the student how to read then you don't need to you can actually use um different ways for them to get that information in other than them reading it themselves okay uh the remedial approach example is if a student listens to a book or has the computer read or scans in a digital version in the book while reading along um and trying to learn unfamiliar words you're improving the areas of deficiency so just know that if you offer it to them in a different way it doesn't mean that that it's cheating it just means that not all kids take in things the same exact way um so assistive technology in a summary Fosters inclusion it facilitated learning experiences it removes barriers to the curriculum and an increase of Independence the most important thing is that we want kids to be able to be independent when they get out of high school and and be able to do things uh on their on their own um if you are in an agency where you guys are working with adults latan is your assistive technology resource out there their services also are free like ours our uh program goes from kindergarten to 12th grade so I just wanted to share latan's website with you guys if any of you guys are working with adults over the age of 21. um this is my contact information thank you so much for listening to my feel about assistive technology um if you have any questions if you want to know more about our program this is our website uh but you can email me directly with any kind of questions and I'm gonna just look um are we able to use able net with unique Learning System absolutely a lot of able Nets program a lot of able Nets products um I actually go hand in hand with unique learning um and and so um because unique learning is the curriculum and ablenet offers some of the tools to access the curriculum but if you have any questions about that or what that would look like uh reach out to me and um you can probably come to our Center and I can actually show you some examples of that um if you're a teacher or if you're a parent helping a teacher um definitely we are here to help you help students um and then I think that's it for my presentation if there are no other questions yeah yeah you actually have until 11 30. Oh I thought it was 11 15. so that's
okay but we did have some q a um okay I can give that to you so um is there a legal requirement that teachers and staff are trained to use the child's technology effectively this is a complaint I hear often from parents that the teacher and AIDS don't know how to use the at right right so you're asking is there a legal requirement so so when the student is considered for augmentative and alternative communication uh typically the parish the district goes through a assistive technology consideration process where they recommend the assist the um the AAC for that student now when students come to school with their AAC device already like designated and the school system did not recommend that device that's where it gets kind of Cloudy you know so um so that's where this the parent could come in and say well I want my child to be evaluated by the school so that the school can deem what system they recommend uh I know a lot of kids nowadays um that are non-verbal will get a private uh private entity to to get them so that you can do it through Medicaid and stuff so here's where you get into issues is if the school system says well that's not the device our team would recommend you know what I mean and so like you're constantly butting heads with we would say this and you would say that so you just have to be on the same page I'm not sure it depends on the district okay and I don't want to get into any kind of legal battles because I'm not a lawyer and I'm just an at facilitator and um all I know is that I know that they there there are districts out there that do really great trainings and that Implement these things really successfully and then there's a lot of schools out there that do don't and so what I want to say about our services is that we are here to help people learn those systems and to help them become fluent so that they can help the child be fluent with those systems because if those people are not modeling the use of that system within the classroom setting all day long then that child will never have the exposure to become fluent with that language so um again about the legal requirement uh I'm just not sure how to answer that question other than saying that the district has policy and procedure in place for at consideration and if the child is non-verbal they have to consider that they have to have it's called the communication plan and so every IEP if that child is non-verbal that that IEP team should be doing that communication plan so if the communication plan states that they need augmentative communication system and and they send one from home then yes they those people on that IEP team need to learn how to use it and so sometimes districts do internal training for that and if they don't have the facility if they don't have the people on staff that know the language they can reach out to us and and we can help them learn it we can send them resources and um we can help them come up with strategies on how to learn it but ultimately they have to model using that system and so that's what's happening is they're not you they're not modeling language through that system and and so um I hope that I kind of answered the legal requirement um so Tim you just had a follow-up question so so what you're saying is um is there legal requirement if the team recommends the device so if they put it in the IEP that student will utilize this um this device or this assistive technology then there is an obligation for the staff to know how to use it right absolutely if it's in the we all know if it's in the IEP it better be happening right um and so a lot of times the district will put that in the IEP and so what the those teams and what parents could maybe do is reach out to us and and you know we could help with the training of the usage of that device because a lot of times people don't know what they don't know and a lot of times when they look at those higher uh high-tech devices um the language looks really foreign and and it's intimidating and people are like oh he can't do that you know they'll have that attitude where the student can't do that no student learns Spanish without being spoken Spanish to you know what I'm saying like if you're teaching a foreign language to a child you have to use that language just like if the child was learning sign language in order to learn that language you have to use that language with that child in the environment a hundred percent of the day so I think that we just need to be diligent with uh our practices and and use the device so um you're not gonna ever learn it if you don't use it so um I'm not sure if you're just how to use okay so someone just said hi Lauren Laura nada I I think I know her um so uh so this is a great uh statement she said and it was about using the at during holiday breaks in the summer um and and um a lot of school districts I don't know exactly specifically which ones but a lot of them have that holiday uh policy in place where they will send the device home with the child um you just have to ask the person at the district the person who is over it all um what's the policy you know what is the take home policy and if they don't have one then I would push for this year being the year they create a take-home policy because again if the student is not being able to use their tool all the time then they're not going to be fluent in using that tool um so I mean there's lots of different Solutions you know to this to this issue and and you just have to work it out we have to learn to work together we're not fighting against each other we should be working together communicating and figuring out what's the best solution for that student because Independence is what we're trying to promote so uh again every school district is different so you really have to reach out to that person in the school district that deals with those decisions if you do not know who that person is reach out to me I have contacts in almost all the districts in the state and I could find out for you who that person is in your child's District that you would talk to directly to get the answers because um you need a better you need to better find out the answers um um follow up on this um said basically a child needs to access their at all times like you said and of course this includes um their homes weekends holidays and over the summer um do kids and their families get this type of access to at which you you answered parents involvement and understanding and assistive technology can make or break a student's educational experience and I think I would go further than just an educational experience I would say their their their life I mean if you don't like communication that's such an impediment um so thank you for that point Jim and I mean what we notice a lot about augmentative communication is that making the decision of which device to use is only one problem the next thing is what language sets do you start with you know so like all of these high-tech augmentative communication devices and I'll I'll show my screen real quick and I'm just showing one to show you what I'm talking about I'm not saying this is the only one but I'm just going to show one right high-tech augmented augmentative communication device it's like once you decide oh this is the late this is the one I'm gonna use the next thing is which uh language organization system am I going to use it's such a lengthy process for deciding and and and the thing about it is is that you're constantly evaluating is this the right one or should I use this one so it's very very important for the speech therapist to be involved in the decision-making process of that language set because they are the language experts I'm a curriculum expert I'm a curriculum person I'm a teacher I don't I'm not I don't have the the background a speech therapist has so it's very very important to be talking to the whole entire IEP team when you're making that decision and when changes happen everybody is in agreement that this is the change needs to happen and it's due to the students needs not the people on the IEP team's needs it's not about the people on the IEP team their needs it's not about oh I can't learn that system sorry you know but but we have a bunch of resources when it comes to learning this new language system um for every different company that's out there they produce a really thorough resource for implementation that teachers power Educators parents everybody should be familiar with when they're learning to model through that system because it's about what we do with the student in the beginning when they're learning it's not what the student can or cannot do it's about what we do as the communication partner to to help that child learn that language system okay so uh I can talk hours for hours about that whole process we don't have enough time but if we have another question can you show where the tools for developing communicate communication plans um is on the Louisiana believes website absolutely okay let me go to that website and and people love it and some people don't and while while the next there's another question too this is great but how does someone keep track of all these choices so that's two questions for you so okay so um when we say someone are we talking about the IEP team or are we talking about family members um any anyone I guess the choices that you're that you was showing like you gave a lot of tools I think this is what I'm understanding okay a lot of resources so how to yes you know just to go through and figure out what's right and where to access it yeah yes presentation um the uh the IEP does have a document uh it has an assistive technology consideration checklist um in the insurs program where it suggests all the different types of assistive technology tools out there and for what they might be used for so uh the IEP team does have a resource built into serve that helps teachers do the assistive technology consideration checklist um we at our Center do have a little assisted technology wheel that uh if you're really if you're going to an IEP and you're like uh I I I just don't know uh we do have a wheel I don't have it at my at my fingertips right now but it's a wheel that talks about all the different kinds of assistive technology and for what you might be using it for um and I could share that with Bambi and she could actually share that out with everybody um so I'm looking at right now the department of education's website and I was being asked to show where that communication thing is and so I'm gonna take you down the road where I would go to get it so I would go to the library of course you can search it uh you can search by communication but I'm going to go library and I'm gonna go category and I'm going to go students with there's a lot of different ways to get to it but I'm gonna go to students with significant cognitive disabilities and I I want to say it's down here under communication but let me just go ahead and check of course it's not it's not on the stage let me go back to and just type in communication plan typically whenever you search things on the doe site sometimes it'll come up see like this is yeah this is not coming up it might be on the second page yeah this is great this is great but um which I think is a excellent point that many people make yeah yeah it's an excellent excellent point that many people make so I'm gonna go so I'm gonna go uh not cognitive disabilities I'm gonna go uh students with disabilities I think it's on this page now the students with disabilities um okay uh communication support okay and so tools for developing communication plans the documents right here so let me go back again just to show you that again Library category students with disabilities go all the way down to you see communication support and then it's here communication plans so this is that document that I'd showed in my presentation and again some districts have taken this document and they've created their own communication plan uh framework for it so if you're in a district and and the communication plan with the IP doesn't look like this one it might be because that District decided to revamp this and and make it a little bit more user friendly but uh in my opinion everything in this document needs to be con needs to be discussed okay and that's just like you know all these questions need to be thoroughly thought about and and reflected on that's why uh pages one through eight are just about Gathering data and then the actual plan itself is on pages 9 10 and 11
2023-08-04 01:02


